Feature Story Imoto Lines and Marindows launch next-generation zero-emission contain…
페이지 정보
작성자 최고관리자 댓글 0건 조회 959회 작성일 24-06-14 16:06본문
- Achieves zero CO2 emissions not only during operation but also within ports and while docked
Scheduled to commence operations in FY2026
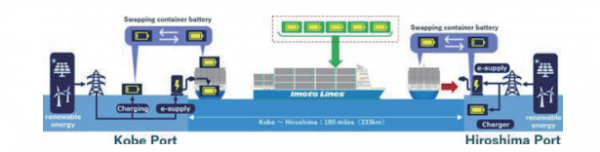
Imoto Lines and Marindows, as a first step in transforming the future of domestic maritime shipping, will build the next generation of zero-emission domestic container ships capable of hybrid operation using Japan's first exchangeable container batteries, alongside onboard batteries, and generators, and conduct demonstration experiments on the Kobe ~ Hiroshima service.
This project is a challenge towards a sustainable future for domestic maritime shipping, aimed at fundamentally solving the three major challenges the industry faces: decarbonization, crew shortage, and safe navigation. The Ministry of the Environment, Government of Japan recognized its value and adopted it as a three-year project for the 'FY2024 Carbon Neutral Technology Research and Development Program'.
Background & Objectives
1. Achieve 'complete zero-emission' CO2 output over the entire lifecycle from fuel mining and manufacturing to usage, not just during operation.
For shippers operating globally, reducing CO2 emissions in the supply chain(Scope 3) is directly linked to international competitiveness, but the use of renewable energy in ships is just beginning to be developed.
This ship will achieve complete zero-emission from fuel mining and manufacturing to usage, by being propelled by renewable energy charged in container batteries.
2. Fundamental resolution to the industry's biggest issue: crew shortage
The domestic shipping industry needs a fundamental solution to the dual shortage of crew numbers and skills.
This ship will achieve safe and efficient navigation with fewer people and less skill/experience required through electrification, thorough standardization and modularization, and land-based support assuming standardization.
3. Cost reduction and value enhancement of next-generation advanced vessels
Next-generation advanced vessels currently under development and introduction are not only expensive but also technologically nascent, carrying the risk of future technology obsolescence(devaluation of vessel value).
This ship will significantly reduce operating costs through thorough standardization, modularization, and mass production, aiming to achieve total operating costs, including construction, that are approximately 30% higher than existing ships, but comparable when overall costs are considered.
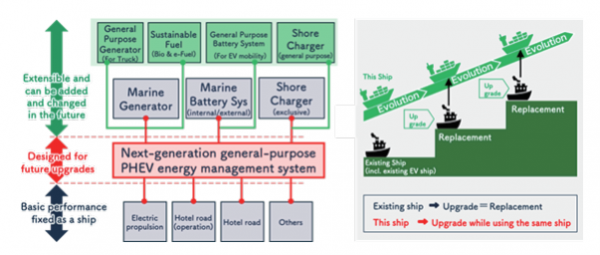
It also adopts a design that can be flexibly upgraded with the introduction of new technologies and systems, minimizing the risk of technology obsolescence = ship obsolescence.
- Technical Development Representative/Joint Implementer: Imoto Lines, Ltd./Marindows Inc.
- Public Support: Ministry of the Environment, Government of Japan Carbon Neutral Technology Research and Development Program
- Project Duration: April 2024 - March 2027
- Demonstration route: Imoto line’s the Kobe ~ Hiroshima service
- Ship Type: Domestic 499 gross tonnage container ship, with a carrying capacity of about 200 TEU(the largest in Japan)
- Completion(Scheduled): January 2027
- Construction Shipyard: Miura Shipbuilding(Saiki City, Oita Prefecture)
- Main Dimensions(Approx.): Length overall 81m / Breadth 13.5m / Depth 6.6m - Speed: 12.5kn(equivalent to 23.2 km/h) / Propulsion Power: 2 x 360kW
- Range: Hybrid (Maximum) - 2,700 miles(5,000km) / Zero-Emission(Standard): 180 miles(333km) using five container batteries / Zero-Emission(Maximum): Depending on the number and capacity of container batteries
- Main Technology Development Elements : EV-optimized ship design exclusively for electric vessels / Standardized and modularized universal plug-in hybrid(PHEV) powertrain / Exchangeable 20-foot container battery system that extends zero- emission range / Standardized and modularized next-generation cockpit system (wheelhouse) and mooring support system for domestic vessels / Land-based support system that assumes standardization / Onshore-to-ship power supply system that not only powers EV ships but also allows existing ships to stop idling while moored / Battery charging and swapping system for container batteries
Five Values Provided by This Project
1. Customer Value Maximization: Not only solves urgent issues for shippers such as CO2 reduction and logistic efficiency, but also provides cost benefits to shippers with virtually the same expenses as existing ships.
2. Environmental Value Maximization: Constructing environmentally friendly ships at virtually the same cost as existing ships.
Achieves zero CO2 emissions during port and docking(idling stop), and will be compatible with complete zero emissions by retrofitting with low environmental impact generators(such as hydrogen fuel cells or bio/synthetic fuels).
Utilization of renewable energy charged in container batteries not only reduces CO2 emissions during operation but also achieves zero emissions over the entire lifecycle(fuel mining, manufacturing, usage).
3. Economic Value Maximization: Mass production becomes possible through standardization and modularization of key equipment and systems, and the introduction of land-based support becomes easier, improving the economic efficiency over the total cost base(ship cost + crew cost + maintenance + fuel cost) compared to existing ships.
4. Crew Value Maximization: Improves the work environment for crew members and enhances productivity per crew member through electrification and standardization/modularization with land- based support. Responds to social issues of an aging population with fewer children, enabling safe and efficient operation even with fewer and less experienced crew members.
5. Unprecedented New Value: The standardization, modularization, and automation of 'Navigation Systems,' 'EV Powertrains,' 'EV-Optimized Ship Shapes,' 'Load Efficiency Improvement,' and 'Digitalization of Operational Information' allow for the benefits of standardization in all aspects of ship construction, ownership, operation, management, and assignment.
Furthermore, the more these standard systems are used and the more ships are added to the fleet, the more they evolve through data accumulation, making next-generation EV ships safer, more efficient, and more environmentally and crew- friendly.
■ Contact: Imoto Lines, Ltd. www.imotoline.co.jp